Zoonotic diseases, also known as zoonoses, are infections that can be transmitted between animals and humans. It can range from mild illnesses like ringworm and salmonellosis to severe and even life-threatening conditions like rabies and Ebola.
Common Routes of Transmission:
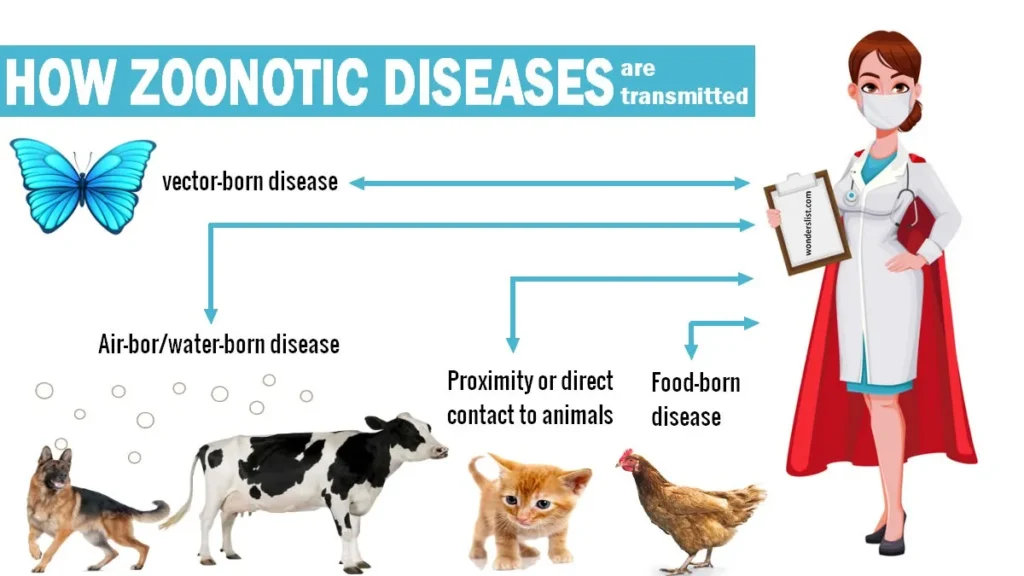
- Direct Contact:
- Bites and scratches from animals (e.g., rabies, cat scratch fever)
- Touching infected animals or their bodily fluids (e.g., saliva, blood, feces)
- Indirect Contact:
- Contact with contaminated surfaces or objects (e.g., pet toys, animal bedding)
- Exposure to contaminated food or water
- Vector-borne Transmission:
- Bites from infected insects (e.g., mosquitoes, ticks, fleas) that transmit diseases like Lyme disease and West Nile virus
Preventing Zoonotic Diseases:
- Proper Hygiene:
- Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water after handling animals, food, or waste.
- Use hand sanitizer if soap and water are not readily available.
- Animal Care:
- Keep pets up-to-date on vaccinations and preventatives (e.g., flea and tick treatments).
- Practice good pet hygiene, including regular grooming and cleaning of living areas.
- Avoid contact with stray or wild animals.
- Food Safety:
- Cook meat and poultry to the recommended internal temperatures.
- Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly before consumption.
- Avoid unpasteurized dairy products.
- Vector Control:
- Use insect repellent containing DEET when outdoors.
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants to minimize skin exposure.
- Regularly check for ticks and remove them promptly.
- Travel Precautions:
- Be aware of potential zoonotic diseases in your travel destination.
- Take necessary precautions to avoid animal contact or insect bites. This may include avoiding contact with stray or wild animals, using insect repellent, and wearing protective clothing in areas known for vector-borne diseases.
If You Suspect a Zoonotic Disease:
- Seek medical attention promptly.
- Inform your healthcare provider about any recent animal contact.
- Follow their instructions for diagnosis and treatment.
Remember:
- Zoonotic diseases are a serious public health concern.
- By taking simple precautions, you can significantly reduce your risk of infection.
- Always consult your healthcare provider or a veterinarian for any concerns regarding animal health and zoonotic diseases.
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge and educational purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical or veterinary advice.




